PrF UG classes class editor
The Class Editor
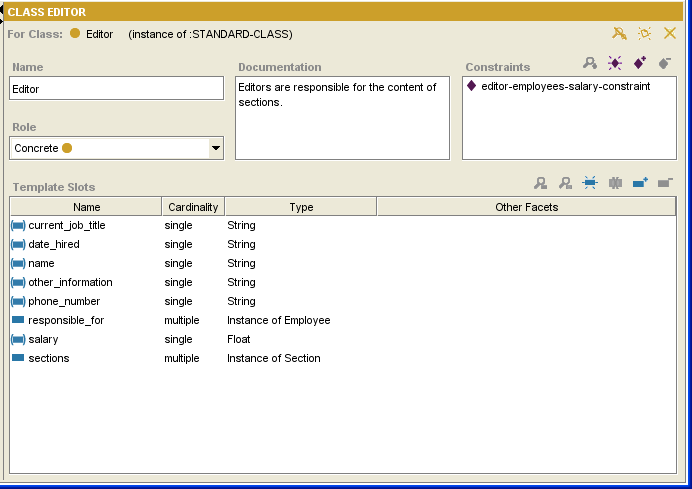
The Class Editor can be used to define and edit the attributes of a class. Click on a link or an area of the picture to jump to a summary. See also Creating a Class, Displaying the Class Editor, Editing a Class, and Editing Template Slots.
Note Icons
The note icons
(![]() ,
,
![]() ,
,
![]() )
at the upper right of the Editor allow you to work with class sticky notes.
These notes, which are not part of your ontology,
can be used for todos or communication while you are developing your knowledge base.
They can be hidden using the Hide Class Notes
(
)
at the upper right of the Editor allow you to work with class sticky notes.
These notes, which are not part of your ontology,
can be used for todos or communication while you are developing your knowledge base.
They can be hidden using the Hide Class Notes
(![]() ) button.
For information on how to add notes to any frame (class, instance, or slot),
see Working with Notes.
) button.
For information on how to add notes to any frame (class, instance, or slot),
see Working with Notes.
Notes are not available when working with the Editor as a free-standing window.
The Class Name Field
The Name field allows you to name your class. When a class is created, it is given a default name, such as newspaper_Class_1. You can change the name of a new or existing class by highlighting the name and overwriting it. The following rules apply to class names:
The name must be a unique class name in the knowledge base.
Class names are case sensitive.
A recommended convention is to make the first character of each word in a class name uppercase and the rest lowercase, and to separate words with underscores.
The Class Role Menu
The Role menu allows you to choose the role of your class: concrete or abstract.
Concrete classes may have direct instances.
Abstract classes cannot have direct instances.
Protege-Frames sets the role to Concrete, by default. Protege-Frames does not impose any restrictions on the role of your classes. One common modeling convention is to make all leaf (bottom-level) classes concrete, and all interior (higher-level, non-leaf) classes abstract.
The Class Constraints Pane
Class constraints are defined programmatically. See Constraints for more information.
The Class Documentation Pane
The Class Documentation pane allows you to enter a text description of the class and other relevant information. These notes are part of your ontology. Filling in this field is optional, but is recommended to aid in the maintenance of the knowledge base.
The Template Slots Pane
The Template Slots pane displays the direct and inherited slots for the selected class. Slots, which represent properties of your class, are a crucial part of your knowledge base. In the example, Editor has several slots which appear in the Template Slots pane. For a full description, see the separate Template Slots pane topic.