Difference between revisions of "PrF UG inst showing subclass instances"
(Automated import of articles) |
|||
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Showing Subclass Instances == | == Showing Subclass Instances == | ||
| − | {{PrF_UG_TOC_inst}}<div id='prf_ug'> | + | <noinclude>{{PrF_UG_TOC_inst}}<div id='prf_ug'></noinclude> |
| − | The | + | The [[PrF_UG_inst_instance_menu|Instance menu]], at the top |
| − | [[PrF_UG_inst_instance_menu|Instance | + | of the [[PrF_UG_inst_instance_browser|Instance Browser]] |
| − | at the top of the | + | allows you to choose the level of instances - |
| − | [[PrF_UG_inst_instance_browser|Instance Browser]] | + | direct instances or subclass instances - you want to see for a selected class. |
| − | allows you to choose the level of instances - direct instances or subclass instances - you want to see for a selected class. | ||
These choices are also available when you are choosing instances in a dialog box. | These choices are also available when you are choosing instances in a dialog box. | ||
| Line 24: | Line 23: | ||
Because of inheritance, | Because of inheritance, | ||
an instance of a class is also an instance of all of that class's superclasses. | an instance of a class is also an instance of all of that class's superclasses. | ||
| − | Therefore, | + | Therefore, an instance can be an instance of many classes |
| − | + | of which it is not a direct instance. | |
</p> | </p> | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
| Line 31: | Line 30: | ||
In the newspaper example, | In the newspaper example, | ||
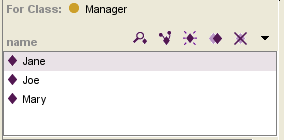
the <b>Manager</b> class has three direct instances: | the <b>Manager</b> class has three direct instances: | ||
| − | Jane, | + | Jane, Joe, and Mary. |
| − | Joe, | + | The <b>Manager</b> class also has a subclass, <b>Director</b>, |
| − | and Mary. | ||
| − | The <b>Manager</b> class also has a subclass, | ||
| − | <b>Director</b>, | ||
which has a direct instance Tim. | which has a direct instance Tim. | ||
Tim is a <i>subclass instance</i> of <b>Manager</b>. | Tim is a <i>subclass instance</i> of <b>Manager</b>. | ||
| Line 41: | Line 37: | ||
=== Showing Subclass Instances === | === Showing Subclass Instances === | ||
| − | By default, | + | By default, the Instance window shows only the direct instances for a class. |
| − | the Instance | ||
| − | <div>[[Image:PrF_UG_inst_show_direct_instances.png| | + | <div>[[Image:PrF_UG_inst_show_direct_instances.png|frame|none| |
| + | Instance window, "Jane" selected]]</div> | ||
| − | You can change this, | + | You can change this, using the Instance menu. |
| − | using the Instance | + | To show all instances for a class, including subclass instances: |
| − | To show all instances for a class, | ||
| − | including subclass instances: | ||
<ol class='a'> | <ol class='a'> | ||
<li><p> | <li><p> | ||
| − | Select <b>Show Subclass Instances</b> from the | + | Select <b>Show Subclass Instances</b> |
| − | + | from the [[PrF_UG_inst_instance_menu|Instance menu]] at the top | |
| − | + | of the [[PrF_UG_inst_instance_browser|Instance Browser]], | |
| − | |||
to the right of the instance buttons. | to the right of the instance buttons. | ||
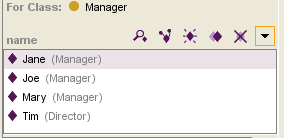
The display will change to show all instances subordinate to the class. | The display will change to show all instances subordinate to the class. | ||
| − | The class for which the instance was created is shown in parentheses after the instance name. | + | The class for which the instance was created |
| − | + | is shown in parentheses after the instance name. | |
</p> | </p> | ||
| + | <div>[[Image:PrF_UG_inst_show_subclass_instances.png|frame|none| | ||
| + | Instance window, showing subclass instances]]</div> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
| Line 68: | Line 63: | ||
<ol class='a'> | <ol class='a'> | ||
<li><p> | <li><p> | ||
| − | It is possible to attach an instance to more than one class (see | + | It is possible to attach an instance to more than one class |
| − | + | (see [[PrF_UG_inst_add_class_type|Adding a Class Type to an Instance]]), | |
so that the instance appears directly under two or more classes. | so that the instance appears directly under two or more classes. | ||
| − | In this case, | + | In this case, the class name displayed after the instance |
| − | + | will be the class where the instance was first created. | |
</p> | </p> | ||
<li><p> | <li><p> | ||
| − | By definition, | + | By definition, abstract classes cannot have direct instances, |
| − | |||
but they <i>can</i> have subclass instances. | but they <i>can</i> have subclass instances. | ||
This selection allows you to see all the subclass instances for an abstract class. | This selection allows you to see all the subclass instances for an abstract class. | ||
| Line 90: | Line 84: | ||
<ol class='a'> | <ol class='a'> | ||
<li><p> | <li><p> | ||
| − | Click on the the | + | Click on the the [[PrF_UG_inst_instance_menu|Instance menu]] at the top |
| − | + | of the [[PrF_UG_inst_instance_browser|Instance Browser]], | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
to the right of the instance buttons. | to the right of the instance buttons. | ||
You will see that <b>Show Subclass Instances</b> is checked. | You will see that <b>Show Subclass Instances</b> is checked. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
</p> | </p> | ||
| + | <div>[[Image:PrF_UG_inst_hide_subclass_instances.png|frame|none| | ||
| + | Show Subclass Instances checkbox (checked)]]</div> | ||
<li><p> | <li><p> | ||
| − | Select <b>Show Subclass Instances</b> from the menu to deselect this setting and show only direct instances. | + | Select <b>Show Subclass Instances</b> from the menu |
| + | to deselect this setting and show only direct instances. | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
| − | </div> | + | <noinclude></div></noinclude> |
Latest revision as of 17:16, November 13, 2008
Showing Subclass Instances
The Instance menu, at the top of the Instance Browser allows you to choose the level of instances - direct instances or subclass instances - you want to see for a selected class. These choices are also available when you are choosing instances in a dialog box.
About Subclass Instances
There are two types of instances subordinate to a class:
A direct instance is an instance that has been created directly under the class.
A subclass instance is any instance that is subordinate to the class. Because of inheritance, an instance of a class is also an instance of all of that class's superclasses. Therefore, an instance can be an instance of many classes of which it is not a direct instance.
In the newspaper example, the Manager class has three direct instances: Jane, Joe, and Mary. The Manager class also has a subclass, Director, which has a direct instance Tim. Tim is a subclass instance of Manager.
Showing Subclass Instances
By default, the Instance window shows only the direct instances for a class.
You can change this, using the Instance menu. To show all instances for a class, including subclass instances:
Select Show Subclass Instances from the Instance menu at the top of the Instance Browser, to the right of the instance buttons. The display will change to show all instances subordinate to the class. The class for which the instance was created is shown in parentheses after the instance name.
Notes:
It is possible to attach an instance to more than one class (see Adding a Class Type to an Instance), so that the instance appears directly under two or more classes. In this case, the class name displayed after the instance will be the class where the instance was first created.
By definition, abstract classes cannot have direct instances, but they can have subclass instances. This selection allows you to see all the subclass instances for an abstract class.
Showing Direct Instances Only
If subclass instances are shown, you can choose to show only direct instances.
Click on the the Instance menu at the top of the Instance Browser, to the right of the instance buttons. You will see that Show Subclass Instances is checked.
Select Show Subclass Instances from the menu to deselect this setting and show only direct instances.