Difference between revisions of "PrF UG inst class browser at instances"
(Automated import of articles) |
|||
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== The Class Browser at the Instances Tab == | == The Class Browser at the Instances Tab == | ||
| − | {{PrF_UG_TOC_inst}}<div id='prf_ug'> | + | <noinclude>{{PrF_UG_TOC_inst}}<div id='prf_ug'></noinclude> |
| − | The Class Browser at the | + | The Class Browser |
| − | [[PrF_UG_inst_instances_tab|Instances | + | at the [[PrF_UG_inst_instances_tab|Instances tab]] |
shows the classes in your knowledge base in a superclass/subclass relationship. | shows the classes in your knowledge base in a superclass/subclass relationship. | ||
When a class with instances is selected, | When a class with instances is selected, | ||
| − | its instances are shown in the | + | its instances are shown |
| − | [[PrF_UG_inst_instance_browser|Instance Browser]] | + | in the [[PrF_UG_inst_instance_browser|Instance Browser]] to the right. |
| − | to the right. | ||
By navigating through the classes, | By navigating through the classes, | ||
you can select the class whose instances you wish to see. | you can select the class whose instances you wish to see. | ||
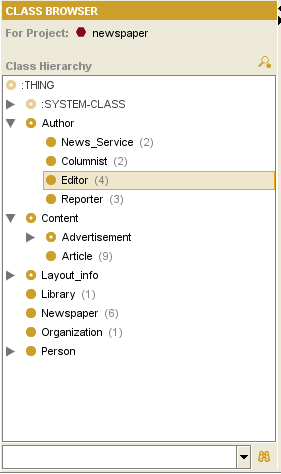
| − | <div>[[Image:PrF_UG_inst_class_browser_instances_tab.png| | + | <div>[[Image:PrF_UG_inst_class_browser_instances_tab.png|frame|none| |
| + | Class Browser, "Editor" selected]]</div> | ||
| − | Parenthesized numbers to the right of a class give information about the number of direct instances that class has. | + | Parenthesized numbers to the right of a class give information |
| − | For example, | + | about the number of direct instances that class has. |
| − | <b>Editor</b> has | + | For example, <b>Editor</b> has four instances. |
| − | If no number is displayed, | + | If no number is displayed, the class does not have any instances. |
| − | the class does not have any instances. | ||
| − | This window is similar to the standard | + | This window is similar |
| − | [[PrF_UG_classes_class_browser|Class Browser]], | + | to the standard [[PrF_UG_classes_class_browser|Class Browser]], |
but you cannot change the hierarchy or add or delete classes. | but you cannot change the hierarchy or add or delete classes. | ||
| − | Therefore, | + | Therefore, there are a number of options that are not available at the Instances tab. |
| − | there are a number of options that are not available at the Instances | ||
| − | <b>Note:</b> You can choose to have {{#var:PrF}} always highlight the class currently selected in the Classes | + | <b>Note:</b> |
| − | To do this, | + | You can choose to have {{#var:PrF}} always highlight the class |
| − | select <b>Windows | Automatically Synchronize Class Trees</b>. | + | that is currently selected in the Classes tab. |
| − | See | + | To do this, select <b>Windows | Automatically Synchronize Class Trees</b>. |
| − | [[PrF_UG_windows_synchronize_trees|Synchronizing Class Trees]] | + | See [[PrF_UG_windows_synchronize_trees|Synchronizing Class Trees]] |
for more information. | for more information. | ||
| − | </div> | + | |
| + | <noinclude></div></noinclude> | ||
Latest revision as of 17:03, November 13, 2008
The Class Browser at the Instances Tab
The Class Browser at the Instances tab shows the classes in your knowledge base in a superclass/subclass relationship. When a class with instances is selected, its instances are shown in the Instance Browser to the right. By navigating through the classes, you can select the class whose instances you wish to see.
Parenthesized numbers to the right of a class give information about the number of direct instances that class has. For example, Editor has four instances. If no number is displayed, the class does not have any instances.
This window is similar to the standard Class Browser, but you cannot change the hierarchy or add or delete classes. Therefore, there are a number of options that are not available at the Instances tab.
Note: You can choose to have Protege-Frames always highlight the class that is currently selected in the Classes tab. To do this, select Windows | Automatically Synchronize Class Trees. See Synchronizing Class Trees for more information.