Difference between revisions of "Using Reasoners"
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
| − | <em>This tutorial assumes a basic working knowledge of Protege-OWL. Please refer first to the [http://www.co-ode.org/resources/tutorials/ProtegeOWLTutorial.pdf Protege-OWL Tutorial] section "4.9 Using a Reasoner". This page explains some additions (e.g. the direct reasoner) that occurred after the publication of the Protege-OWL tutorial.</em> | + | <em>This tutorial is a brief users guide for using reasoners in Protege-OWL. It assumes a basic working knowledge of Protege-OWL. Please refer first to the [http://www.co-ode.org/resources/tutorials/ProtegeOWLTutorial.pdf Protege-OWL Tutorial] section "4.9 Using a Reasoner". This page explains some additions (e.g. the direct reasoner) that occurred after the publication of the Protege-OWL tutorial.</em> |
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
== Using the DIG Reasoner == | == Using the DIG Reasoner == | ||
| + | |||
| + | The DIG interface is a standard interface/protocol that was introduced to provide a common interface to DL reasoners. In this way, applications, such as Protege-OWL, can access several reasoners by using a common interface. | ||
| + | The current version implemented by several DIG compliant version is [http://dl-web.man.ac.uk/dig/2003/02/interface.pdf DIG 1.1], which has a number of know flaws (e.g. very limited support for datatypes, etc.). See [http://www.hpl.hp.com/techreports/2004/HPL-2004-85.html this paper] for more details. There is a [http://dig.cs.manchester.ac.uk/roadmap.html roadmap] for the 2.0 version of DIG that would address these limitations, however it is not clear when this version will become available. | ||
=== Getting the DIG-compliant reasoner === | === Getting the DIG-compliant reasoner === | ||
| Line 49: | Line 52: | ||
If instead of that, you see an almost empty panel with a red text: '''''Reasoner Error: Connection refused''''', it means that you have not configured correctly the Reasoner URL in the OWL Preferences or the reasoner is not running. | If instead of that, you see an almost empty panel with a red text: '''''Reasoner Error: Connection refused''''', it means that you have not configured correctly the Reasoner URL in the OWL Preferences or the reasoner is not running. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Using the Direct Reasoner == | ||
Revision as of 16:47, April 18, 2008
Using DL reasoners in Protege-OWL
This tutorial is a brief users guide for using reasoners in Protege-OWL. It assumes a basic working knowledge of Protege-OWL. Please refer first to the Protege-OWL Tutorial section "4.9 Using a Reasoner". This page explains some additions (e.g. the direct reasoner) that occurred after the publication of the Protege-OWL tutorial.
Contents
Using the DIG Reasoner
The DIG interface is a standard interface/protocol that was introduced to provide a common interface to DL reasoners. In this way, applications, such as Protege-OWL, can access several reasoners by using a common interface. The current version implemented by several DIG compliant version is DIG 1.1, which has a number of know flaws (e.g. very limited support for datatypes, etc.). See this paper for more details. There is a roadmap for the 2.0 version of DIG that would address these limitations, however it is not clear when this version will become available.
Getting the DIG-compliant reasoner
First, you need to make sure that you have downloaded a DIG compliant reasoner, such as:
- Pellet - open source, implemented in Java
- Fact++ - open source, implemented in C++
- RacerPro - commercial
- KAON2 - commercial, free of charge for universities and for noncommecial academic usage
Second step is to install the reasoner and start the DIG HTTP service. Please read the documentation of the reasoner to see how to start the DIG service.
Configure the DIG reasoner URL
Then you need to configure the port on which the reasoner DIG service is running. The most common port used by the reasoner is 8080, and that is also the default configuration for Protege-OWL. If the reasoner runs on this port (which you can usually figure out from the console window in which the reasoner is running), then you can skip this step. If however, the reasoner runs on a different port (e.g. Pellet runs by default on 8081), then you need to do the following steps:
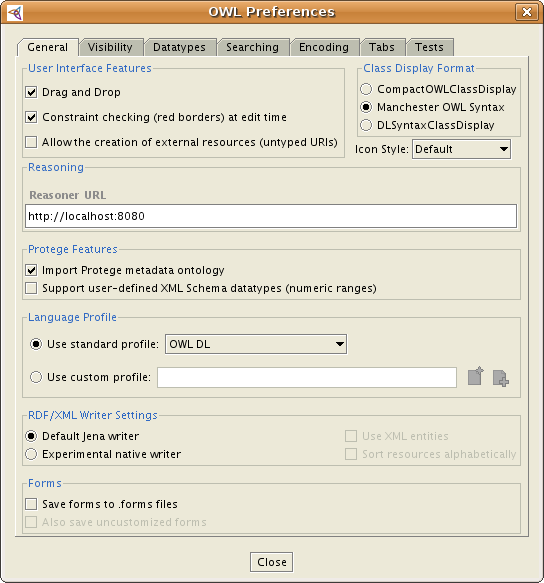
Go to the OWL Menu -> Preferences -> General Tab and in the Reasoner URL text field adjust the URL and port on which the reasoner is running.
For example, if Pellet would run on localhost and port 8081, then the reasoner URL should be: http://localhost:8081.
Classifying the ontology
Now you are ready to test the reasoner connection and to classify the ontology.
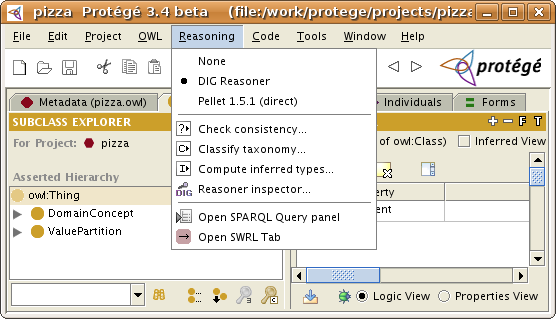
First, make sure that "DIG Reasoner" is selected in the Reasoning menu (the default selection when you install Protege). The Reasoning menu allows you to select which is the current reasoner that should be used when the users classifies the ontology, checks the consistency, computes the inferred types, etc. from the user interface.
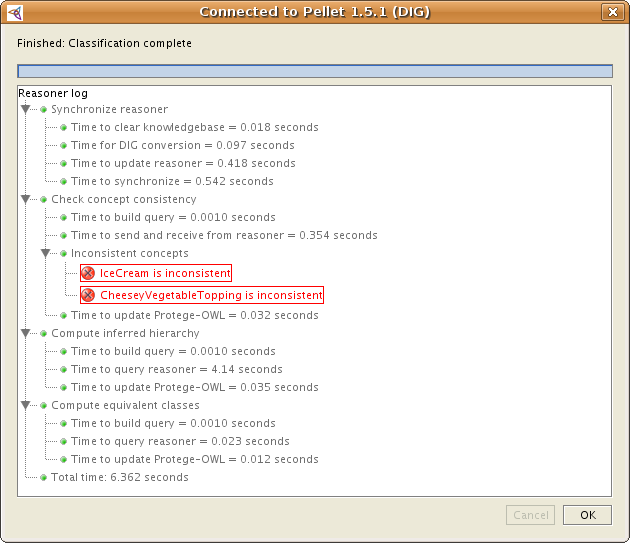
To classify the ontology, select "Classify taxonomy" in the Reasoning menu. You should see a panel coming up that has a title: Connected to Pellet x.y.z (DIG)
If instead of that, you see an almost empty panel with a red text: Reasoner Error: Connection refused, it means that you have not configured correctly the Reasoner URL in the OWL Preferences or the reasoner is not running.