Protege4Views
Protege 4.x Views
This page contains a summary of the default views provided with Protege 4.x, many of which are not visible by default.
Back to Protege4UserDocs
Contents
- 1 General views
- 2 Views by category
- 2.1 Class views
- 2.2 Data property views
- 2.3 Individual views
- 2.4 Misc views
- 2.5 Object property views
- 2.6 Ontology views
- 2.6.1 Annotations
- 2.6.2 DL metrics
- 2.6.3 Explanation
- 2.6.4 Inferred axioms
- 2.6.5 Navigation subject
- 2.6.6 Navigation view
- 2.6.7 Ontology metrics
- 2.6.8 Rules
- 2.6.9 Imported ontologies
- 2.6.10 OWLViz imports graph
- 2.6.11 Manchester syntax rendering
- 2.6.12 OWL functional syntax rendering
- 2.6.13 OWL/XML rendering
- 2.6.14 RDF/XML rendering
- 2.6.15 FaCT++ Rendering
Views are the building blocks of the P4 user interface. They can be placed anywhere on any tab and your setup will be persisted across P4 versions.
For notes on how to configure your user interface to include some of these views please see this section in our quick start guide.
Views are to be found in the View menu, and are categorised as below.
General views
Some views are very similar for multiple categories (particularly those for different entity types), and are therefore cross-referenced to here to avoid duplication.
Hierarchy views
The primary means of navigating around an ontology is the various hierarchy views that are shown on the left of a tab by default.
Selecting an entity in its tree causes a global selection update (making it possible to go back and forward like a web browser). Other views that can show entities of the same type will refresh to display information pertinent to that entity.
Most trees support drag and drop - the effect of which depends on the type of information shown by the tree.
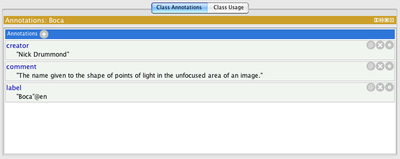
Annotations views
Classes, properties, individuals, ontologies and even axioms can be annotated. All of the views look and act the same way.
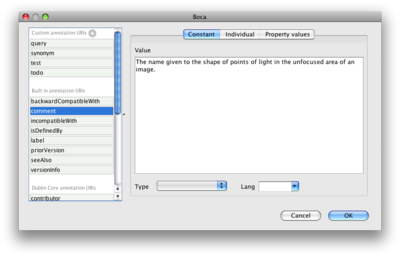
Clicking Add, double clicking on an existing annotation or clicking its edit button opens the editor (below).
Annotation editor
Select an annotation URI from the left (or add your own on in the top section if you want).
You can annotate using:
- Constant a data value (typed or untyped). If untyped, then you can specify a language.
- Individual an existing named individual from the ontology (you can even create one in the editor
- Property values an anonymous individual (one that can have properties itself, but is not visible outside the ontology - arguably they should only be visible in this editor)
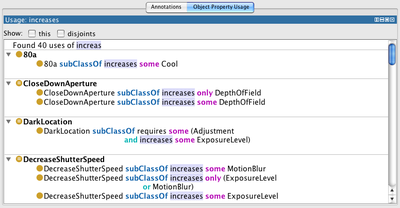
Usage views
For classes, properties and individuals the usage view shows anywhere in the active ontologies that references the currently selected entity.
Usage is sorted by referencing entity (where possible) and all expressions are hyperlinked for easy navigation.
This can be particularly useful for finding out how much a particular entity is used in an ontology, or when you want to know where a class has been used as the filler of a restriction for example.
There are additional filters also available to reduce the results:
- this axioms that pertain to the current selection and are likely to be easily visible in other views. eg when p is selected, functional(p) is hidden unless the this box is checked
- disjoints the number of disjoints can be large (particularly if they are pairwise) and are often not helpful in understanding the use of a property/class so are hidden unless this box is checked
- named sub/superclasses (for classes only) this information is easily read off the class hierarchy and a large number of subclasses clutters the usage view so they are hidden unless this box is checked
Views by category
Class views
Asserted class hierarchy
Also see Hierarchy Views
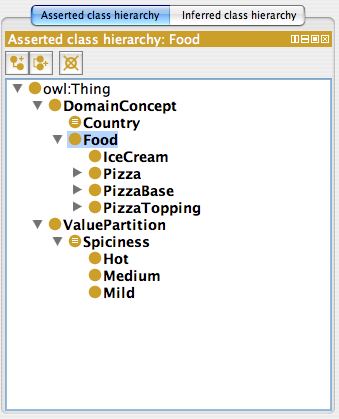
The asserted class hierarchy view is one of the primary navigation devices for named OWL classes.
The tree shows the subclass hierarchy that can be obtained from subClassOf assertions in the ontology. Children nodes in the tree are subsumed by their parent nodes. Any classes that do not have an asserted superclass will show up directly under owl:Thing (the root). For convenience, the tree also performs some trivial inferences to allow defined classes to appear in the hierarchy. Classes that have been asserted to be equivalent show up together on the appropriate node in the tree. Cycles are detected and removed.
Classes will show up multiple times in the tree if they have more than one asserted named superclass.
Primitive classes are shown with a simple circle icon. Defined classes are shown with an equivalence symbol in their icon.
Dragging and dropping classes in the hierarchy will cause subclass relations to change (the old subclass relation will be removed and a new one added).
Inferred class hierarchy
Also see Hierarchy Views
Similar to the Asserted class hierarchy but using the reasoner to provide a complete view.
The inferred class hierarchy will be empty unless a reasoner has been selected and the ontology successfully classified.
By default, after classification, the inferred class hierarchy will be brought forward if it is hidden behind another view (as it is by default).
To avoid confusion, it has been made easy to recognise this view by its pale yellow background and the fact that it contains an additional class owl:Nothing not shown in the asserted class hierarchy. In OWL Nothing is defined as the empty set - a class that is unsatisfiable. Classes that have been inferred to be unsatisfiable will be marked in red and shown as children of Nothing.
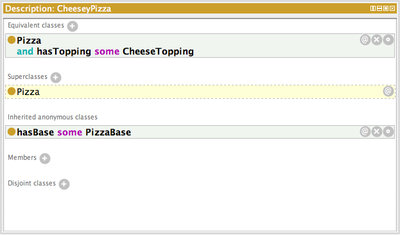
Description
The class description view is the core of the class editor. A combination of asserted and inferred information is shown in this view. Inferred information in pale yellow with a dashed border.
The sections are
- Equivalent classes each entry specifies a named class or expression that is equivalent to the current selected class
- Superclasses each entry specifies a named class or expression that is a superclass of the current selected class
- Inferred anonymous superclasses protege searches all ancestors of the selected class and accumulates all of their anonymous superclasses which are then displayed in this section
- Members each entry specifies an individual that has this class as its type in a class assertion axiom
- Disjoint classes each entry specifies a single disjoint statement. A disjoint statement can contain 2 or more classes (the current selected class is removed from the list for clarity)
Adding or editing Equivalent classes or Superclasses invokes a dialog that contains multiple editors. The editors range from a simple tree from which a class can be picked, to restriction creators that help produce simple restrictions with a named filler, to a fully functioning expression editor. The editor set is pluggable so developers can add further tool support.
The Disjoint classes editor gives the choice of a class hierarchy on which multi-select can be performed, or an expression editor where multiple values can be entered by comma separating them.
Many entries in this view can be right clicked (select first, then right click on a mac) for a contextual menu that allows several options depending on the type of thing selected.
- Switch to defining ontology make the ontology that contains this assertion the active ontology
- Pull into active ontology move the assertion into the current active ontology
- Move axiom(s) to ontology move the assertion(s) into a specified ontology
- Convert selected rows to defined class build an intersection using the selected superclasses and make this class equivalent to the intersection (removing the superclass assertions)
- Create new defined class make a new defined class that is equivalent to the selected class
- Create closure axiom (if the assertion is subclassOf(p some A)) accumulate all fillers of superclass some restrictions on p (say A, B and C). Add a new superclass - p only (A or B or C) to close the property p.
Annotations
Usage
See Usage views
Asserted superclass hierarchy
Also see Hierarchy Views
The asserted superclass hierarchy is an inverted tree. With the currently selected class as its root, all children in the tree are asserted superclasses of their parent, right back to owl:Thing at each leaf node.
This can be useful in tracking where multiple superclasses have been asserted (considered bad modelling practice).
Inferred superclass hierarchy
Also see Hierarchy Views
Similar to the Asserted superclass hierarchy but using the reasoner to provide a complete view.
General class axioms
OWLViz
Anonymous defined classes
An experimental feature not currently available. See this page about anonymous class support
Data property views
Data properties
Annotations
Usage
See Usage views
Characteristics
Description
Domains and ranges
Individual views
Description
Annotations
Usage
See Usage views
Individuals
Individuals by class
Members list
Property assertions
Misc views
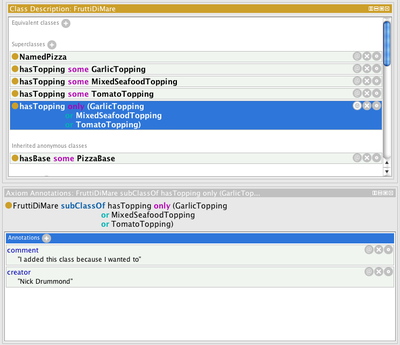
Axiom annotations
Inline view for viewing/editing axiom annotations. See axiom annotations for more information.
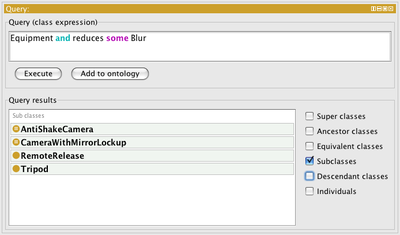
Query
Better known as DLQuery.
Selected entity
The basis for the entities tab.
This view contains other views and follows the current selection, whether this is a class. property or individual.
The default layout for each entity type can be seen in the entities tab - you can completely change these and they will be preserved.
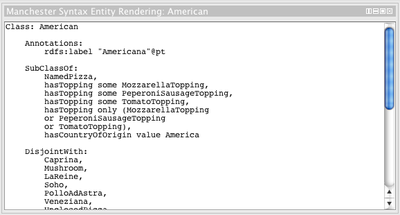
Manchester syntax entity rendering
Coming in build 105. Manchester syntax rendering for the currently selected entity (for easy cut and paste).
Object property views
Annotations
Characteristics
Description
Domains and ranges
Usage
See Usage views
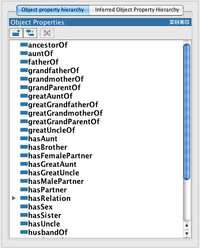
Object properties
The primary object property hierarchy.
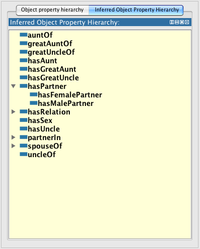
Inferred object property hierarchy
Once the reasoner has classified this view will show the computed property hierarchy.
Ontology views
Annotations
DL metrics
Explanation
Inferred axioms
Ontology metrics
Rules
Imported ontologies
OWLViz imports graph