BeanshellView
BeanshellView
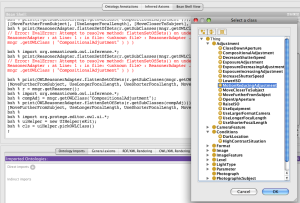
Some coding just doesn't justify setting up an entire java build environment. Some coding requires immediate feedback. Using the Beanshell view, any user can now access the power of the P4 to query and manipulate ontologies or even interact with the UI.
Most of P4 can be accessed from the OWLEditorKit or OWLModelManager (variables eKit and mngr respectively).
For more information see the Beanshell Website
Contents
Versions & Compatibility
This section lists available versions of BeanshellView.
| Version | Compatible with | Dependencies |
|---|---|---|
| BeanshellView 1.1.1 | Protege-OWL 4.2 Protege-OWL 4.1 | |
| BeanshellView 1.0.0 | Protege-OWL 4.0 |
If you click on the button below to add a new version of BeanshellView, you will be asked to define a page title for the new version. Please adhere to the naming convention of BeanshellView X.X.X when you define the new page!
Changelog
| Version | Changes in this version |
|---|---|
| BeanshellView 1.1.1 | see page for more details |
| BeanshellView 1.0.0 | see page for more details |
Examples
Here are some code examples you could try
Creating a new class in the current ontology
ont = mngr.getActiveOntology();
fac = mngr.getOWLEntityFactory();
changes = fac.createOWLClass("myNewClass", ont.getURI());
mngr.applyChanges(changes.getOntologyChanges());
Check if the current ontology is valid OWL DL
import org.semanticweb.owl.profiles.*; dlProfile = new OWLDLProfile(); ont = mngr.getActiveOntology(); dlProfile.checkOntology(ont, mngr.getOWLOntologyManager()); report = dlProfile.checkOntology(ont, mngr.getOWLOntologyManager()); print(report.isInProfile());
nonDLConstructs = report.getDisallowedConstructs();
for (c : nonDLConstructs) {
print(c);
}
Pick a class to use in a script
uiHelper = new UIHelper(eKit); c = uiHelper.pickOWLClass(); print(c);
Use a reasoner
First make sure a reasoner has been selected and the ontology is classified.
import org.semanticweb.owl.inference.*; r = mngr.getReasoner(); c = // get your class here - for example as above subs = OWLReasonerAdapter.flattenSetOfSets(r.getSubClasses(c)); print(subs);
Note the use of OWLReasonerAdapter as the reasoners return equivalence sets.