Difference between revisions of "Working with the Database Backend in OWL"
(→Converting a Project to a Database Project) |
|||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
== Before you start == | == Before you start == | ||
| − | This example requires that the mysql jdbc drivers are available to Protege. To make the drivers available, download the drivers from [http://smi-protege.stanford.edu/repos/protege/protege-core/trunk/dbdrivers/mysql-connector-java-5.0.0-beta-bin.jar here], copy the jar file into the Protege installation directory and call it driver.jar. | + | This example requires that the mysql jdbc drivers are available to Protege. To make the drivers available, download the drivers from [http://smi-protege.stanford.edu/repos/protege/protege-core/trunk/dbdrivers/mysql-connector-java-5.0.0-beta-bin.jar here], copy the jar file into the Protege installation directory and call it driver.jar. In theory, any jdbc database should work but we have only done testing for mysql, postgres, oracle 9g and the microsoft sql server. The drivers for all of these options can be found [http://smi-protege.stanford.edu/repos/protege/protege-core/trunk/dbdrivers here]. |
== Opening an ontology using a web uri == | == Opening an ontology using a web uri == | ||
Revision as of 13:14, April 21, 2008
Working with the Database Backend in OWL
Contents
Before you start
This example requires that the mysql jdbc drivers are available to Protege. To make the drivers available, download the drivers from here, copy the jar file into the Protege installation directory and call it driver.jar. In theory, any jdbc database should work but we have only done testing for mysql, postgres, oracle 9g and the microsoft sql server. The drivers for all of these options can be found here.
Opening an ontology using a web uri
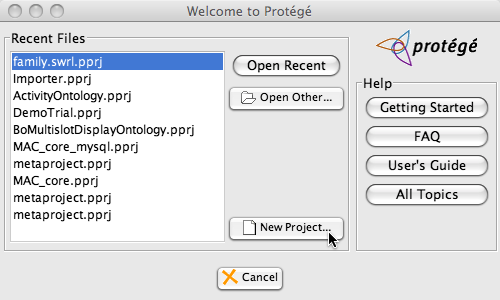
This note will show by example how to convert an owl project and its imports to a database backend project. We will use the proton ontology as an example because it has a few non-trivial imports. The first step is to open it from the web. We start protege and in the welcome screen we select "New Project".
Note that if Protege is already open and you don't see the welcome screen then you can access the screen below by clicking on the File menu and selecting "New Project".
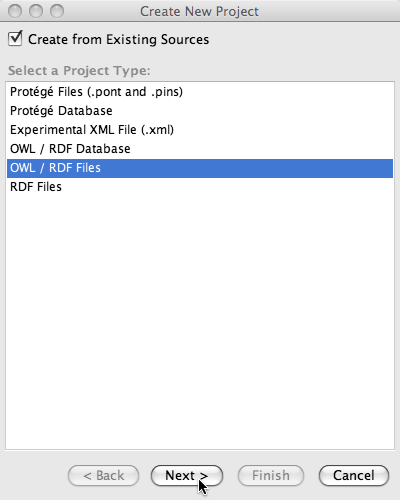
Now since we want to create a Protege OWL project using a url from the internet, we
- select Use existing sources,
- select OWL/RDF Files and
- click next.
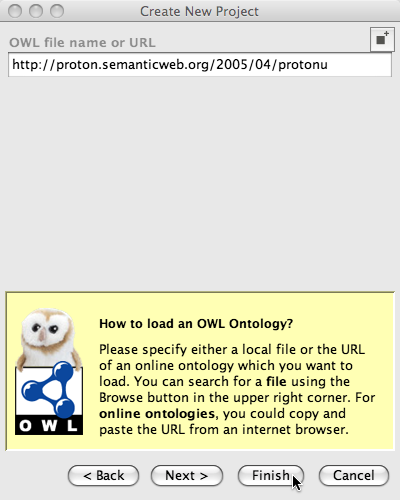
Finally we enter the url (http://proton.semanticweb.org/2005/04/protonu) for the upper Proton ontology and click finish.
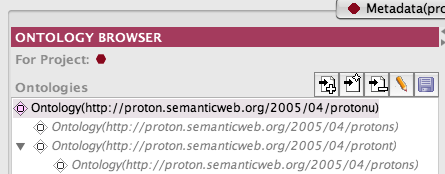
Wait a bit and the ontology will come up. When it does, you will see the reason that this ontology was chosen for this demonstration when you unravel the imports in the imports tab. There are two imports (protont and protons) which occur in two different places.
Converting a Project to a Database Project
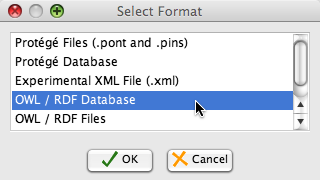
Now we will convert the upper Proton ontology to a database project. To do this click on the Protege File menu and select "Convert Project to Format". In this window select the "OWL / RDF Database" format and click ok.
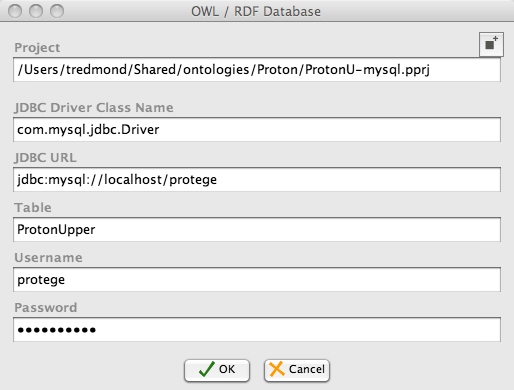
Once you click ok, you will see a dialog with several database settings. You can fill them as shown below.